
EASTER ORDERS ARE CLOSED!
Wishing everyone a Happy Easter
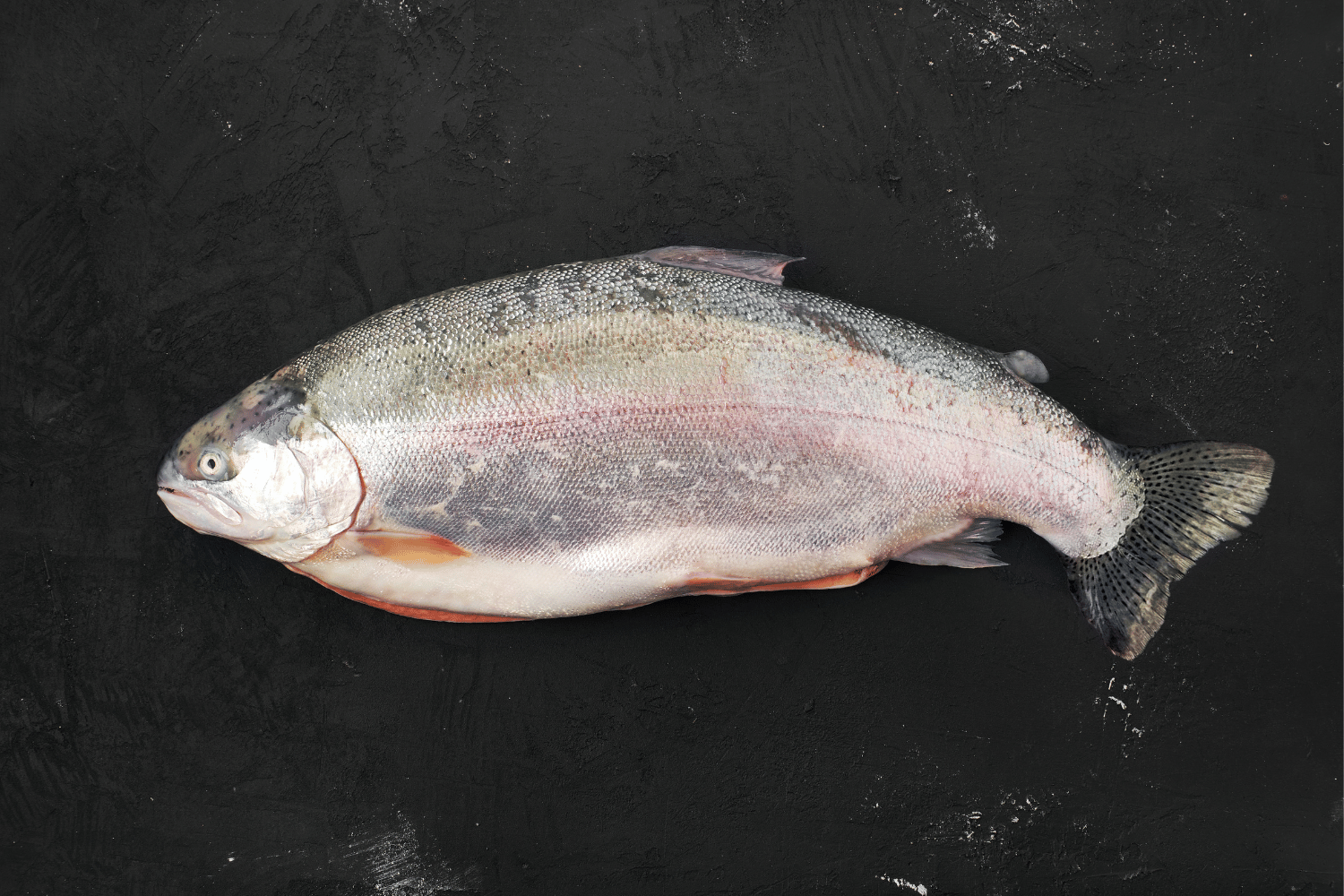


Trout and salmon are two of the most popular fish in the world, and for good reason. They’re both delicious, nutritious, and versatile. But what’s the difference between the two?
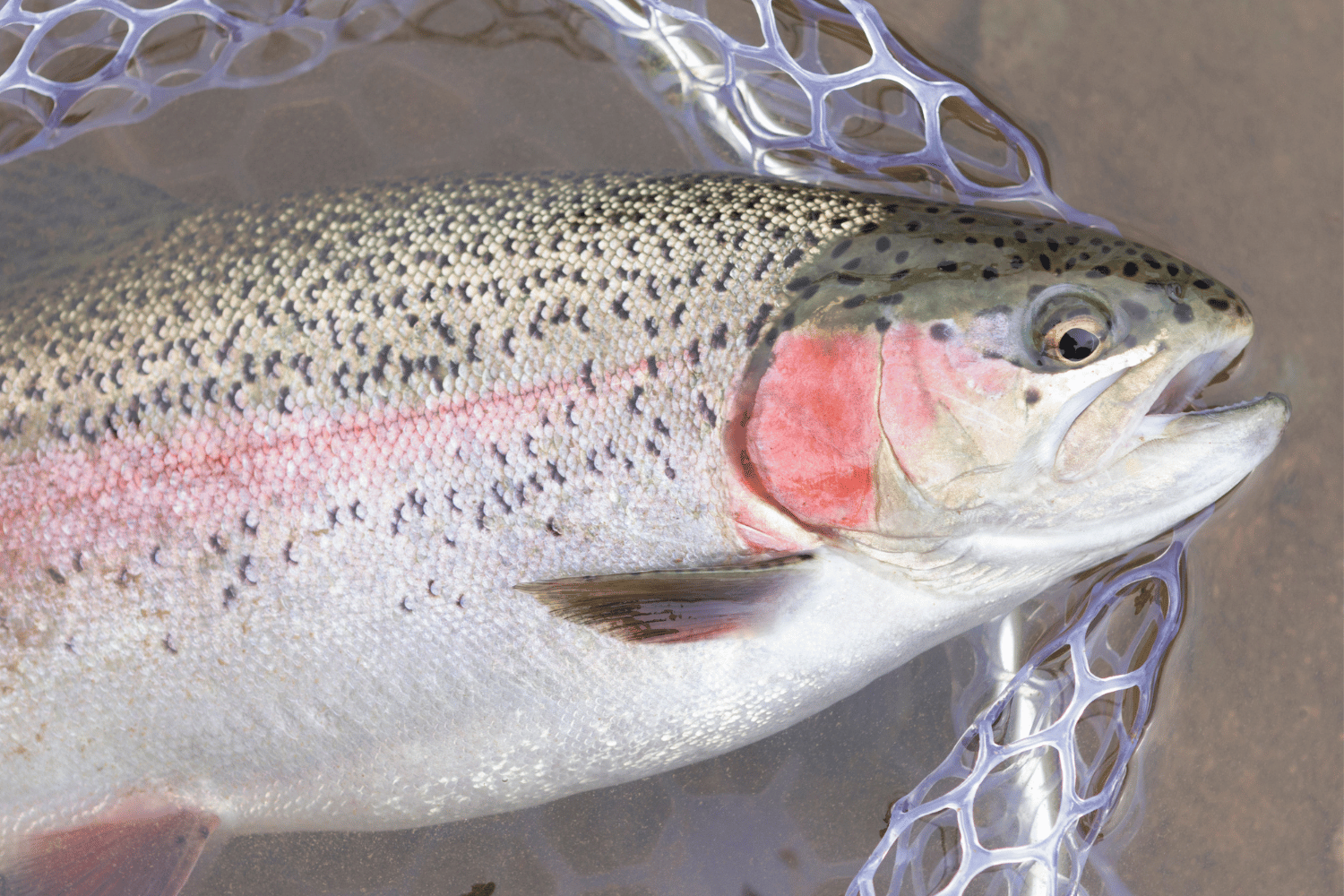
Trout are freshwater fish that belong to the salmon family. They’re found worldwide, and there are many different species of trout. Some of the most popular types of trout include rainbow trout, brown trout, and steelhead trout.
Salmon are, of course, also members of the salmon family. Salmon are anadromous fish, which means they spend part of their lives in freshwater and part of their lives in saltwater. Salmon are born in freshwater streams but migrate to the ocean to grow and mature. After several years at sea, they return to their freshwater birthplace to spawn.
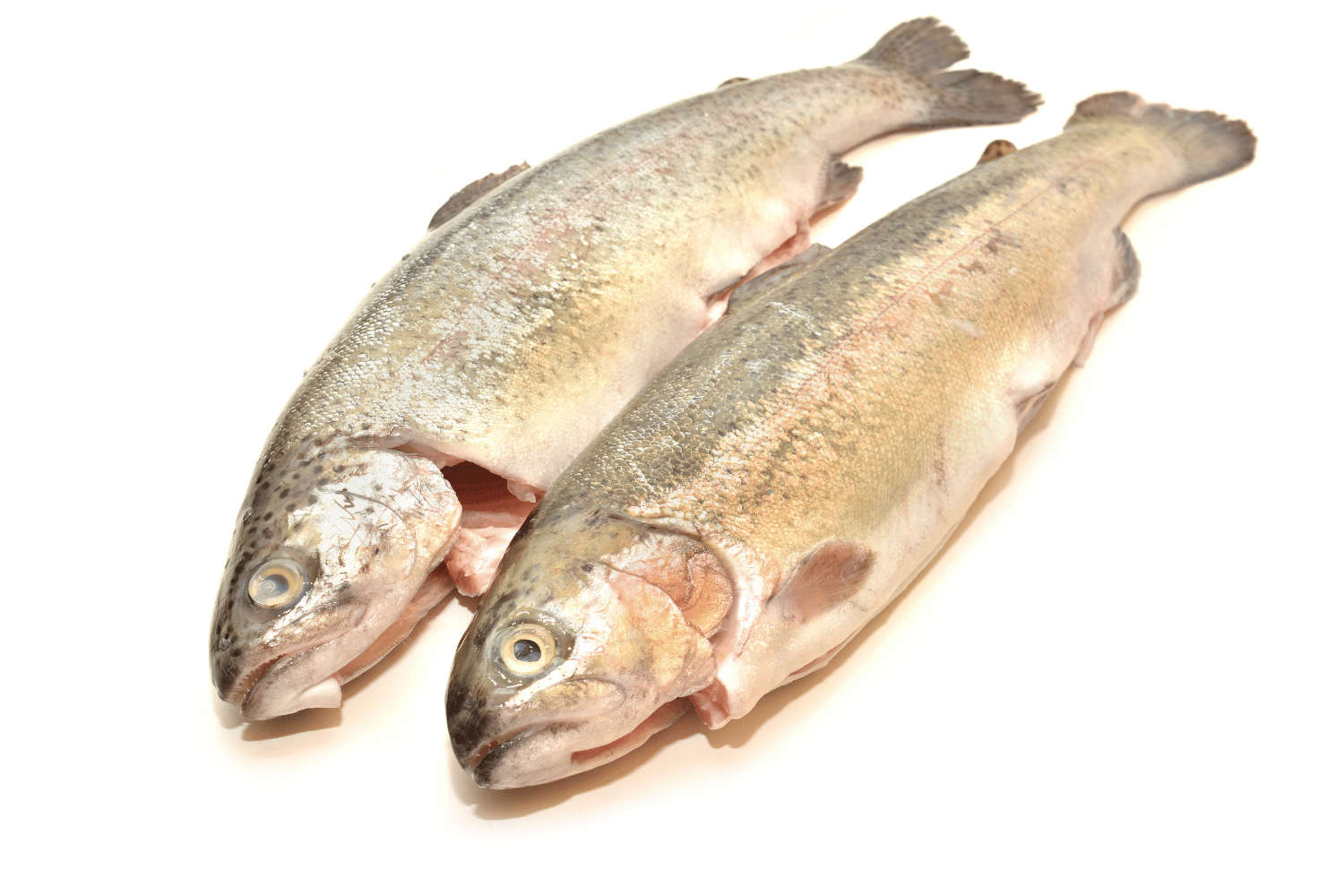

Rainbow Trout
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s establish a foundation of knowledge about trout and salmon.
Trout are a diverse group of freshwater fish known for their vibrant colours and remarkable adaptability. The most common trout species include:
In addition to the four species mentioned above, many other species of trout are found worldwide. Some of these other species include:
Trout are an important part of the aquatic ecosystem and play a vital role in the food web. Trout are also a popular recreational and commercial fish species.
Salmon are a diverse group of fish that can thrive in both freshwater and saltwater habitats. Some of the most popular salmon species include:
All salmon species are a good source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and other nutrients. They are also relatively low in calories and saturated fat. Ora King salmon is a healthy and versatile food that can be enjoyed in many ways.
Here are some additional facts about salmon species:
Now that we’ve introduced you to some common trout and salmon species, let’s explore their physical characteristics and what makes them different from one another.
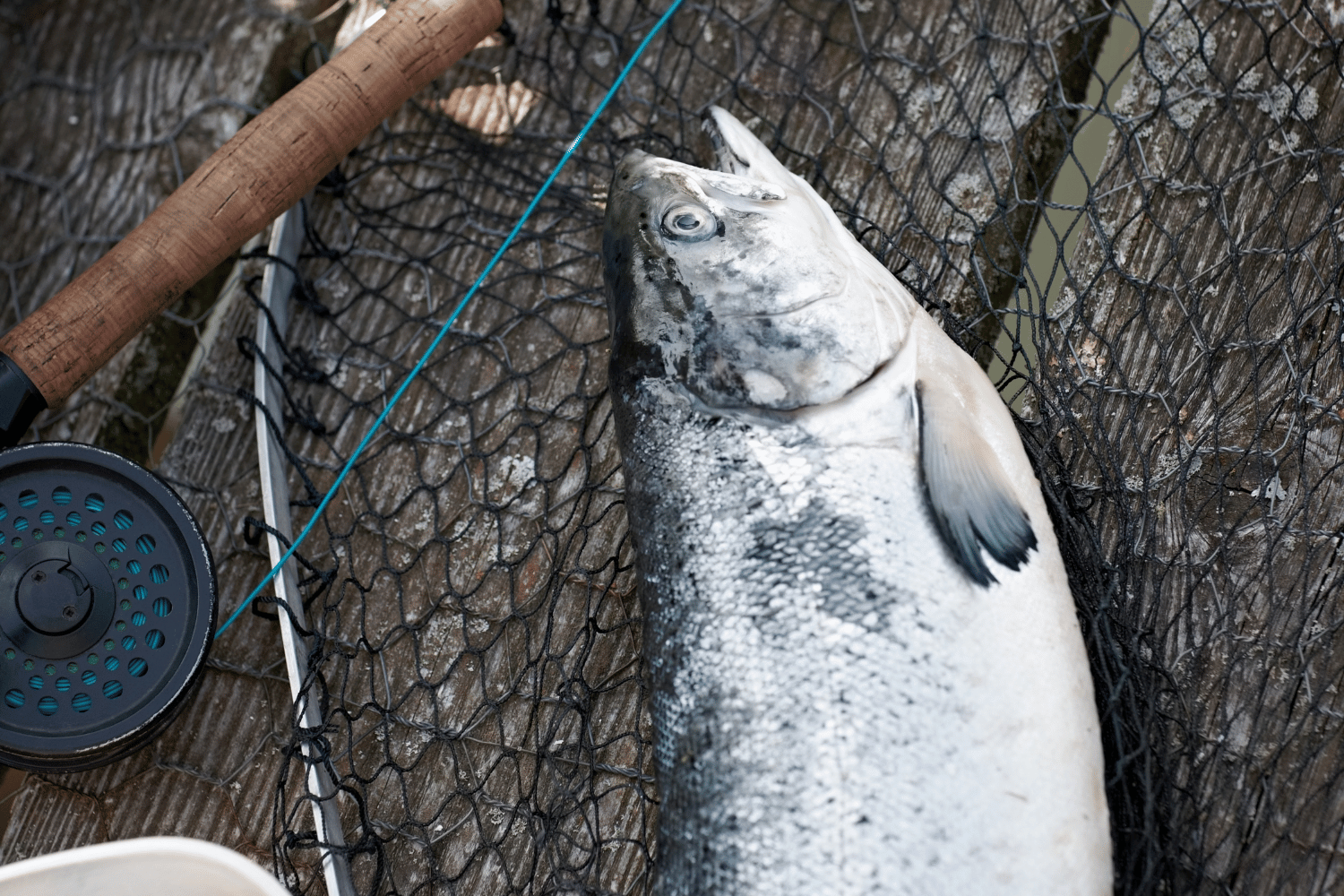

Freshly caught trout

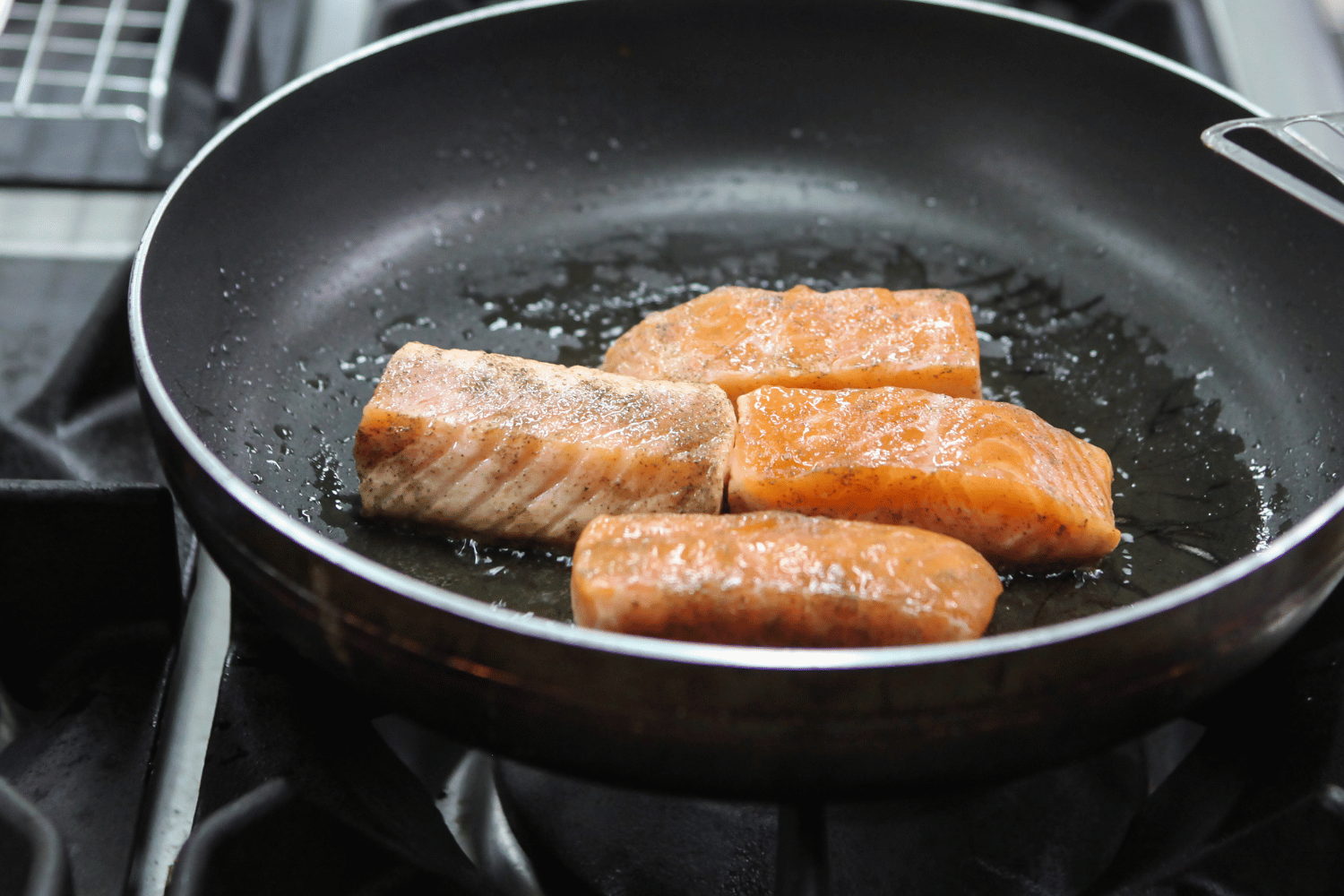
Freshly caught salmon
When it comes to taste, trout and salmon offer unique experiences for your palate.
Trout is celebrated for its mild, delicate flavour. It has a subtle sweetness that pairs beautifully with various seasonings and cooking methods. Whether pan-fried with herbs or grilled with a lemon-butter sauce, cooking with trout offers you many different flavoursome options.
Salmon boasts a richer flavour profile compared to trout. Its high-fat content gives it a luxurious, buttery taste that can withstand bold seasonings and sauces. From simple preparations like salmon fillets with a drizzle of olive oil to more complex dishes, salmon suits a range of flavour profiles depending on your own unique tastes and preferences.
Nutritional Value
Both trout and salmon are packed with essential nutrients, making them an excellent choice for a balanced diet.
Trout is a lean fish with a mild flavour and a flaky texture. It is a good source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins B6, B12, and D, and minerals such as potassium, selenium, and phosphorus. Trout is also a low-calorie food, with about 120 calories per 85-gram serving.
Salmon is a fatty fish with a richer flavour and a more oily texture than trout. It is an excellent source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins B6, B12, and D, and minerals such as potassium, selenium, and phosphorus. Salmon is also a good source of vitamin A. An 85-gram serving of cooked salmon contains about 175 calories.
Trout and salmon both offer a number of health benefits, including:
When choosing trout and salmon, it is important to consider the following factors:
Fresh vs frozen: Both fresh and frozen trout and salmon can be healthy choices. However, fresh fish is generally considered higher quality than frozen fish.

Trout and salmon are delicious and versatile fish that can be cooked in various ways. However, there are a few key differences between the two that you should keep in mind when cooking.
Trout and salmon can be cooked using various methods, including baking, grilling, pan-frying, and poaching. However, some methods are better suited for one type of fish.

Here are a few recipes for cooking trout and salmon that will help to get you inspired.
Baked Trout with Lemon and Herbs
Ingredients:
Instructions:
Ingredients:
Grilled Salmon with Soy Sauce and Garlic
Ingredients:
Instructions:
As responsible seafood consumers, it’s important to consider sustainability when choosing between trout and salmon.
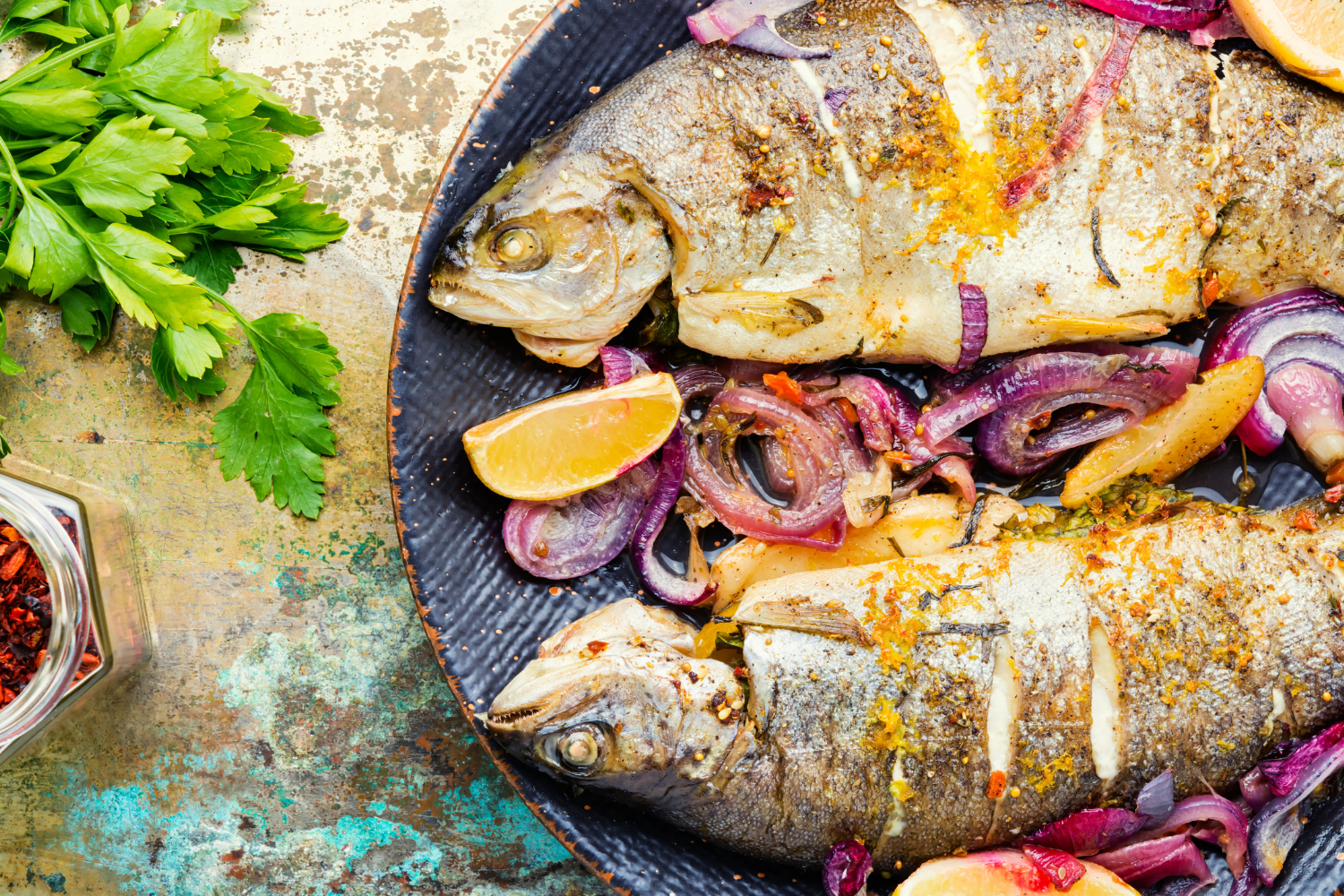

Trout and salmon are two fish species that offer distinct flavours and culinary possibilities. Whether you prefer the delicate taste of trout or the rich, buttery goodness of salmon, both fish have their place on the dining table. At Manettas Seafood Market, we celebrate the diversity of Australia’s seafood offerings and provide access to a wide range of high-quality, sustainably sourced fish.
Making a conscious choice about the seafood you enjoy not only adds variety to your diet but also contributes to the sustainability of our oceans. So whether you’re grilling trout by the lake while camping, or baking salmon at home in your kitchen, you’re making a positive impact while indulging in the delights of the sea.
For more information on trout, salmon, and other seafood options, explore our extensive selection at Manettas Seafood Market.