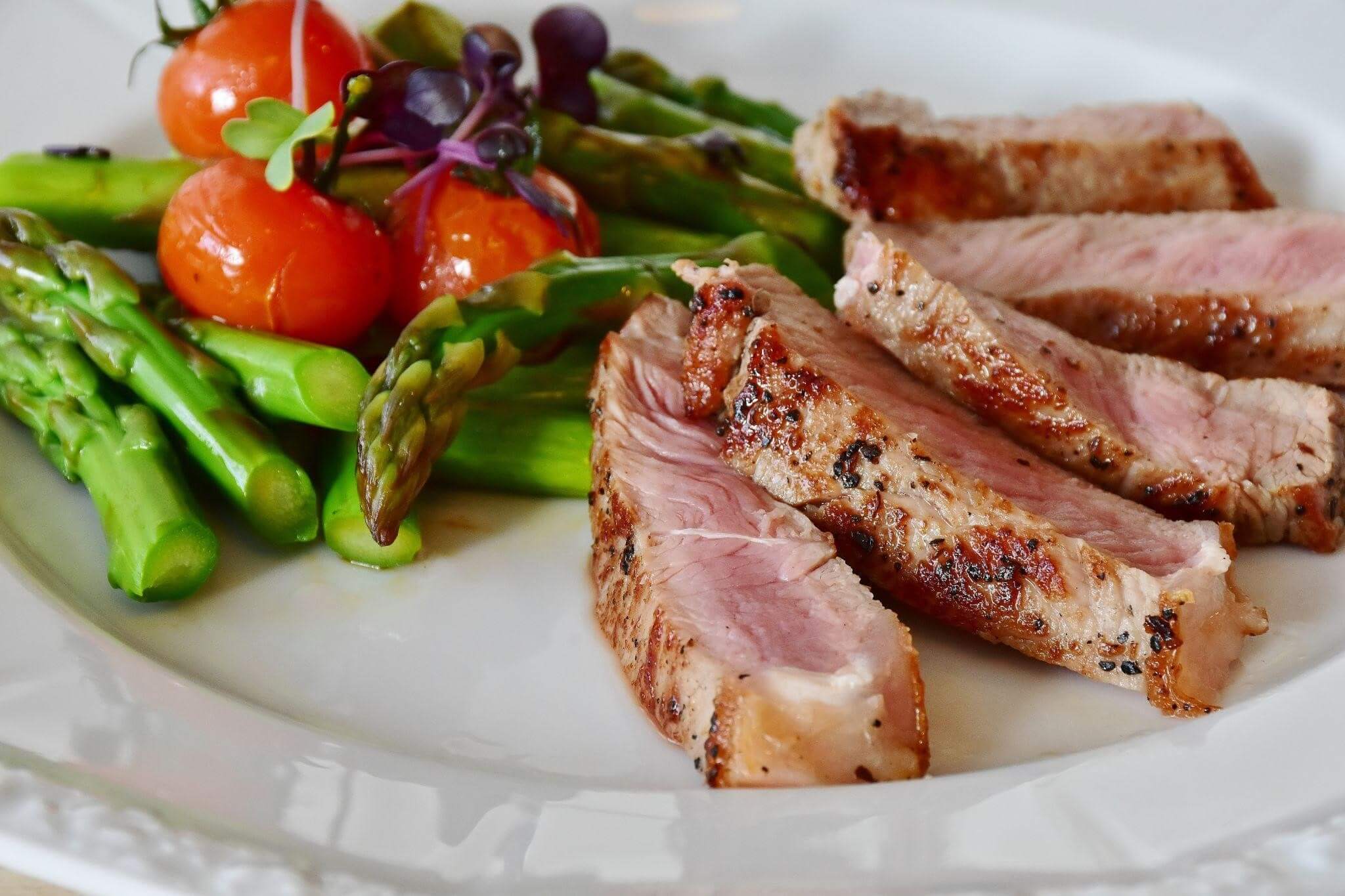



Eat meat and always go for a well-balanced diet.
Meat has long been a staple of the Australian diet with it being a vital piece of our food culture and tradition. In fact, we’re among the world’s top meat-eating countries, with an average of 95 kgs of meat consumed per capita each year.
With people becoming more and more health-conscious over the past few years, there has been some debate about the health benefits of eating meat. While statistics show that our zest for meat is alive and well, it’s important to explore the nutritional value of meat and why it truly is an essential part of a healthy diet.
Meat is packed with important nutrients that your body needs to function at its peak. But not all meats are created equal when it comes to nutrition. Apart from the type of meat, you also need to consider the specific cut of meat. Pork loin and beef sirloin, for example, are lean cuts, making them a wonderful addition to your diet.
Meat can be classified as either white meat or red meat, depending on the type of animal it comes from. White meat is typically found in poultry, such as chicken and turkey, while red meat is found in beef, pork, lamb and other mammals.
While white meats are considered healthier than red meat, the latter is also an excellent source of essential nutrients.
Here some of the key nutritional benefits that you might expect to find in various meats:
Protein is also important for maintaining strength and muscle mass, making meat an ideal food option for people who engage in a lot of physical activities.
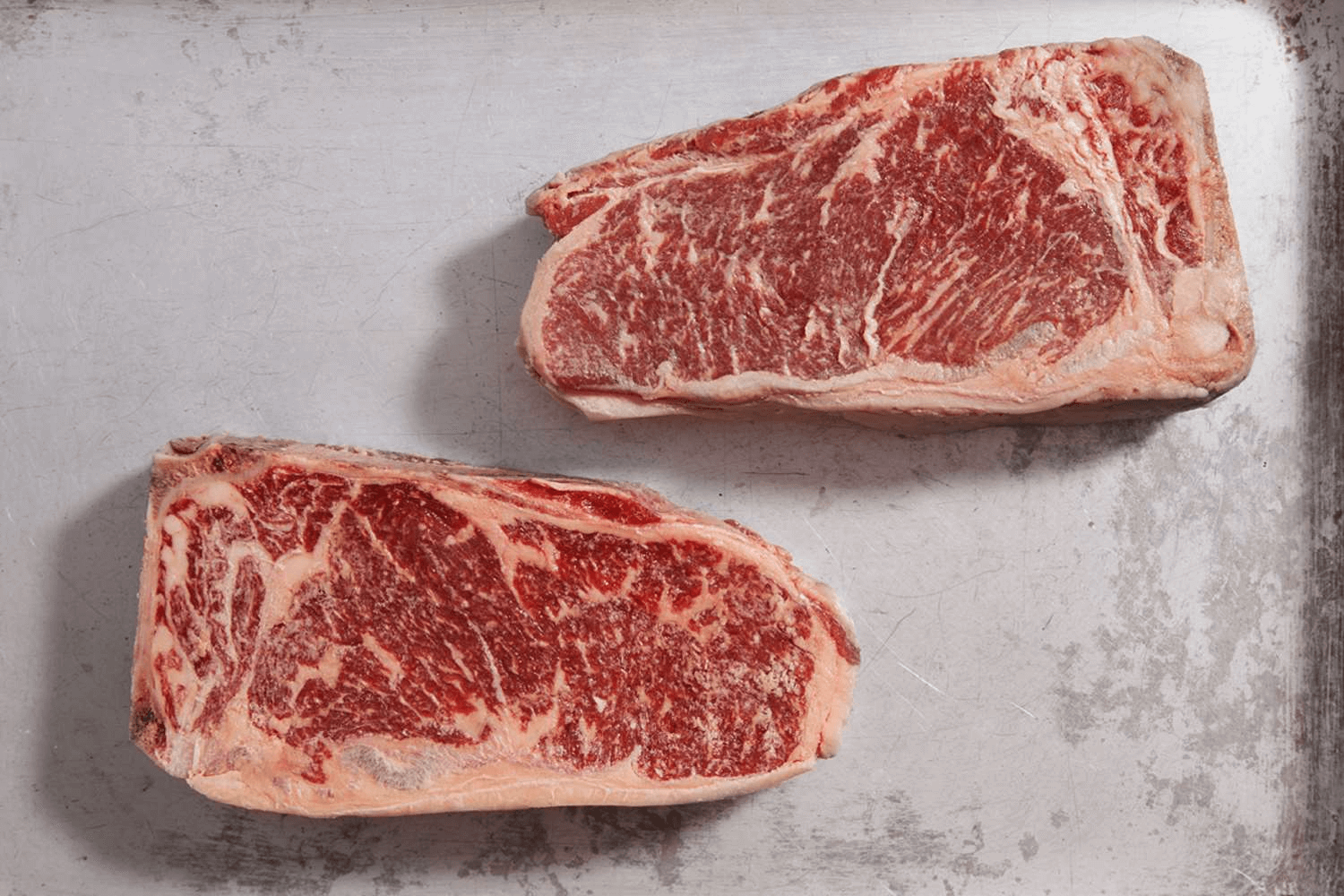

Want your beef on the bone? Try this rib sirloin from grain-fed cattle.
Meat is an important source of nutrients that can provide many positive benefits to our health. With its generous nutritional value, it plays a significant role in nurturing our mind and body.
With its high protein content, meat helps repair muscle damage and supports muscle growth and strength. The Australian Dietary Guidelines point to a maximum of about seven serves of lean red meat per week. To maximise your intake of quality protein, combine lean meat with fish, eggs, beans, legumes, nuts and seeds.
Meat is a good source of tyrosine, a natural amino acid and precursor to dopamine, which is responsible for transmitting messages between the nerve cells in your brain and the rest of your body.
Fatty fish and meat from grass-fed animals contain high levels of omega-3 fatty acids which are essential for brain development and function through every stage of our life. Furthermore, meat is rich in Vitamin B12, choline and zinc, which all play significant roles in brain health.
Meat contains several nutrients that are important for maintaining healthy bones. Apart from protein, it also contains calcium, vitamin D, phosphorus and magnesium.
Protein is known to be more satiating than carbohydrates or fats, and may help to increase the number of calories burned throughout the day by boosting the metabolic rate. Lean meats, such as chicken and turkey breast, are relatively low in calories compared to other protein sources, and thus can be a good option if you want to better manage your weight.
In addition, some studies suggest that consuming a higher protein diet may lead to increased fat loss and improved body composition compared to diets lower in protein.
The satiating effects of meat are due to its high protein content, which triggers the release of hormones that signal fullness to the brain. It has been known to stimulate the release of satiety hormones, such as cholecystokinin, which promote feelings of fullness and curb appetite.
Protein is more satiating than carbohydrates, meaning it can help you feel fuller for longer and reduce your overall calorie intake.
It’s worth noting that some meats can be high in calories and saturated fat, so it’s important to choose lean cuts and consume them in moderation (as with any food) as part of a balanced diet. It’s also wise to limit your processed meat consumption as this has been linked to various health risks.
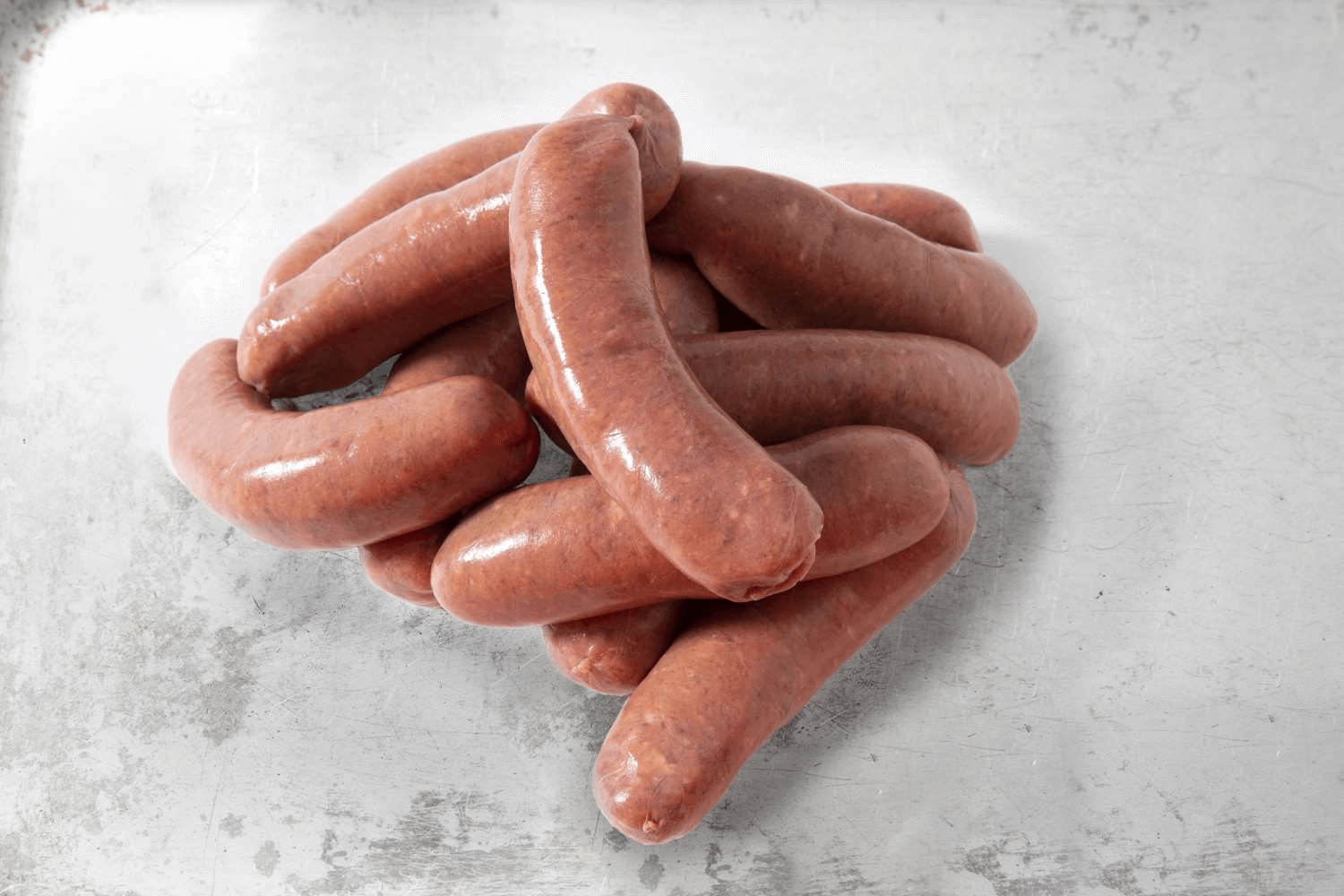

If you really like sausages, make sure they’re made of the highest-quality meat. Try these beef sausages from the highly respected Andrews Meats.
While some cooking methods have been associated with potential health drawbacks, there are ways to reduce the risk. One way is to choose a cooking method that involves lower temperatures and less direct exposure to flames.
For example, baking, boiling and slow cooking can all be effective methods for reducing exposure to unwanted chemicals. Marinades have also been shown to reduce the formation of such chemicals, so you might want to marinate your meat before cooking.
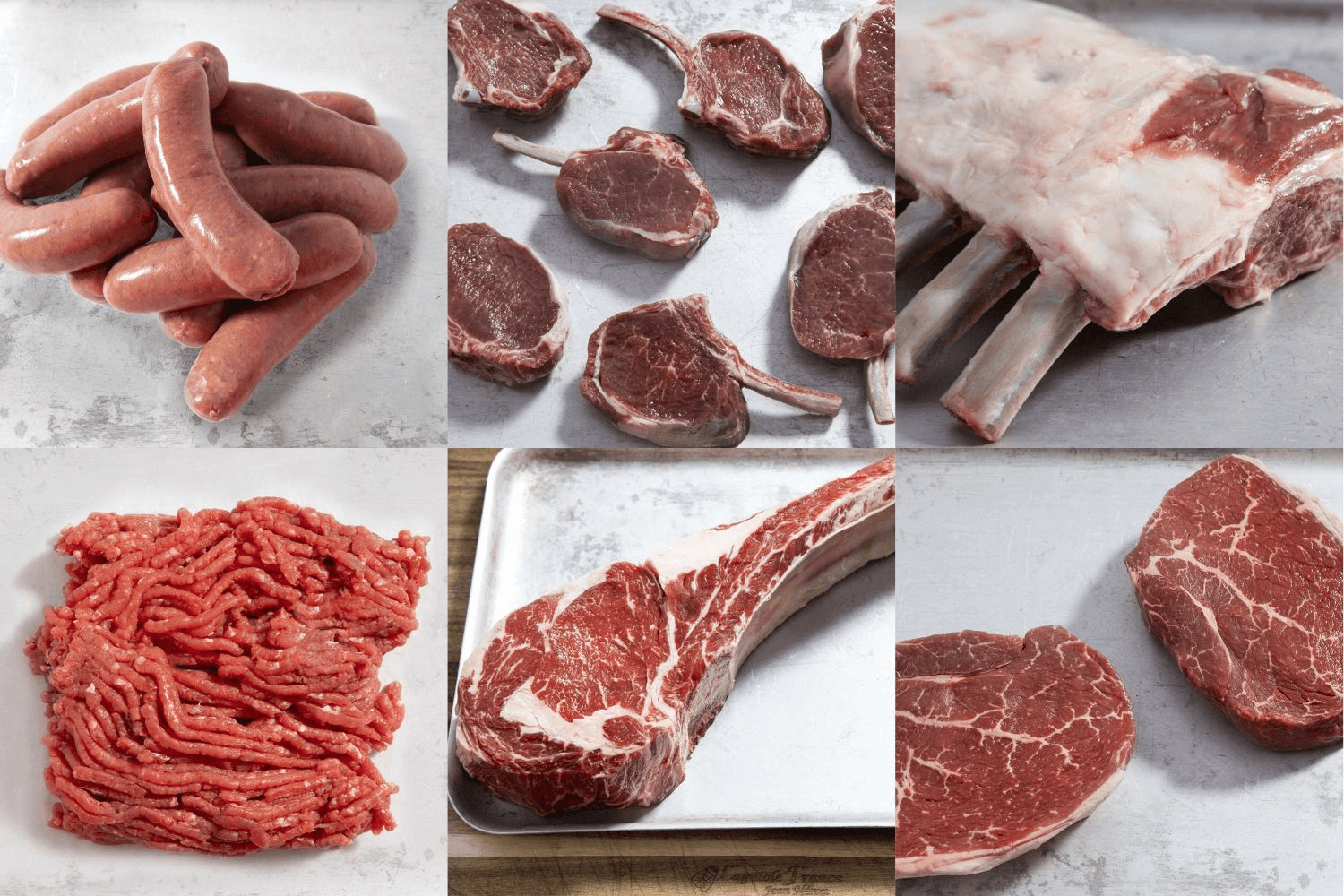

The Andrews Meat Selection Box is a true meat lover’s favourite.
It’s possible to reduce fat before and during preparation. Here are a few ways to do it:
Cook your meat all the way through to prevent harmful bacteria that can cause food poisoning. With thoroughly cooked meat, you’ll ensure there won’t be any pink or red meat left inside, whether it’s sausages, kebabs, rolled joints of meat and other meat products.
Moreover, you don’t want to reheat meat more than once, as this may also lead to food poisoning.
Can meat form part of a healthy diet? It certainly can! Both white and red meat are important in our diet and can have a tonne of positive effects on our health. So, why not elevate your dining experience by incorporating your choice of high-quality beef, pork, fish, poultry or lamb from Manettas Seafood Market? Indulge in the finest meats while supporting your health and savouring every delectable bite.